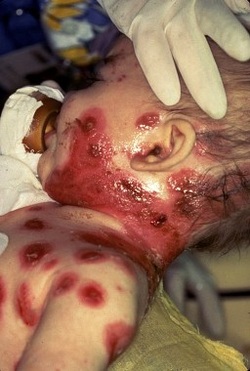
Varicella
Description
A disease caused by infection with the varicella zoster virus, which causes fever and an itchy rash
Symptoms
A skin rash of blister-like lesions, covering the body but usually more concentrated on the face, scalp, and trunk. Most, but not all, infected individuals have fever, which develops just before or when the rash appears. If exposed, persons who have been vaccinated against the disease may get a milder illness, with less severe rash (sometimes involving only a few red bumps that look similar to insect bites) and mild or no fever.
Complications Bacterial infection of the skin, swelling of the brain, and pneumonia. Adolescents and adults are more at risk for severe disease.
Transmission
Spread by coughing and sneezing (highly contagious), by direct contact, and by aerosolization of virus from skin lesions.
Vaccine Varicella vaccine can prevent this disease. Currently, two doses of vaccine are recommended for children, adolescents, and adults.
Who Needs to be Vaccinated?
All children and adults without evidence of immunity to varicella need the vaccine. Evidence of immunity includes any of the following:
A disease caused by infection with the varicella zoster virus, which causes fever and an itchy rash
Symptoms
A skin rash of blister-like lesions, covering the body but usually more concentrated on the face, scalp, and trunk. Most, but not all, infected individuals have fever, which develops just before or when the rash appears. If exposed, persons who have been vaccinated against the disease may get a milder illness, with less severe rash (sometimes involving only a few red bumps that look similar to insect bites) and mild or no fever.
Complications Bacterial infection of the skin, swelling of the brain, and pneumonia. Adolescents and adults are more at risk for severe disease.
Transmission
Spread by coughing and sneezing (highly contagious), by direct contact, and by aerosolization of virus from skin lesions.
Vaccine Varicella vaccine can prevent this disease. Currently, two doses of vaccine are recommended for children, adolescents, and adults.
Who Needs to be Vaccinated?
All children and adults without evidence of immunity to varicella need the vaccine. Evidence of immunity includes any of the following:
- Documentation of two doses of varicella vaccine
- Blood tests that show you are immune to varicella or laboratory confirmation of prior disease
- Born in the United States before 1980, excluding health-care workers, pregnant women, and immunocompromised persons. These individuals need to meet one of the other criteria for evidence of immunity.
- Receipt from a healthcare provider of a) a diagnosis of chickenpox or b) verification of a history of chickenpox
- Receipt from a healthcare provider of a) a diagnosis of herpes zoster (shingles), or b) verification of a history of herpes zoster (shingles).